Oral Presentation 21st International Conference on Biological Inorganic Chemistry 2025
Carboplatin-Based Pt(IV)-Deferoxamine Conjugates as Multifunctional Agents for Cancer and Infection Theranostics (#272)
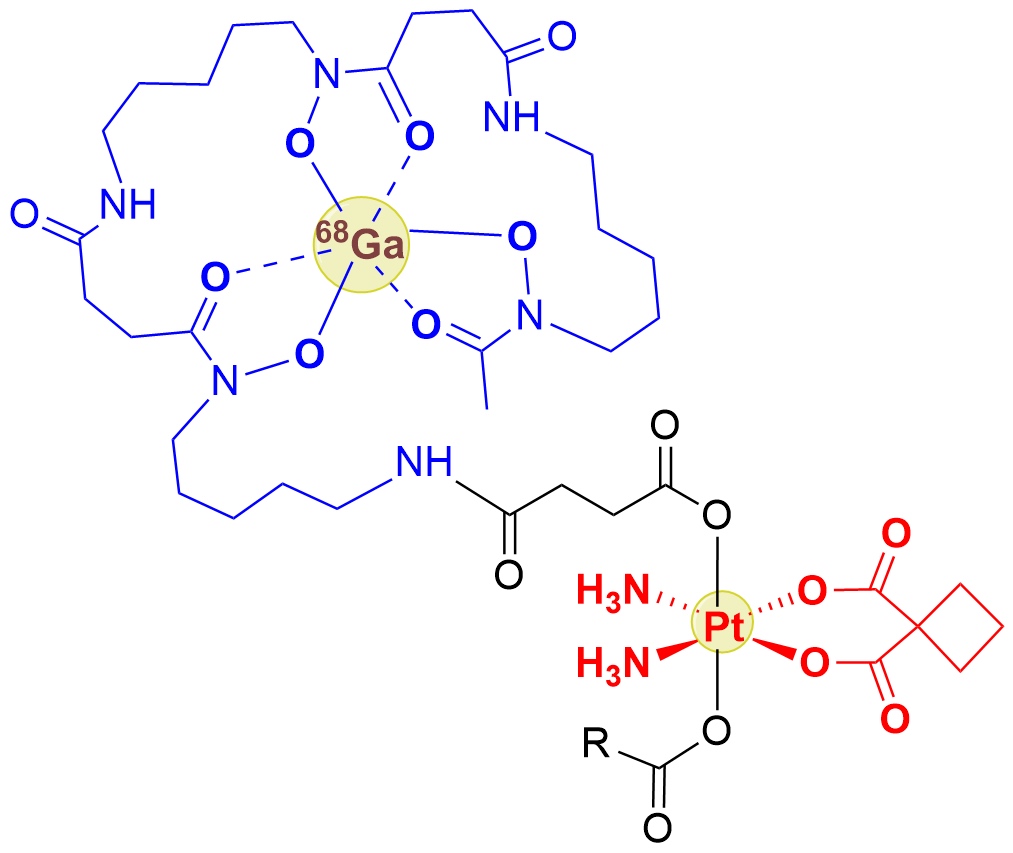
Platinum(IV) complexes bearing bioactive axial ligands offer a promising platform for developing multifunctional prodrugs that expand the therapeutic potential of platinum-based chemotherapeutics. The synergistic interaction we previously observed between the anticancer drug carboplatin and the iron chelator deferoxamine (DFO) in lung cancer cell lines1 provided the initial motivation for designing Pt(IV) prodrugs capable of co-delivering both agents. Such compounds also offer potential for molecular imaging via radiolabelling, as well as targeted antimicrobial activity against pathogens expressing siderophore transporters (SITs) that recognize DFO.
A series of Pt(IV) complexes incorporating the carboplatin core and one or two DFO units at axial positions were synthesized, thoroughly characterized, and evaluated for cytotoxicity in both 2D and 3D cancer cell models.2 Two lead compounds were radiolabeled with gallium-68 and evaluated by radio-HPLC for serum stability and in vivo metabolism following administration to mice. In vitro uptake and antifungal activity were investigated using Aspergillus fumigatus (AFU) and a SIT1-deficient mutant strain.3
The Pt(IV)–DFO conjugates demonstrated favorable physicochemical characteristics but only moderate cytotoxicity across the tested cancer cell models.2 The DFO moiety retained its chelating functionality, enabling efficient 68Ga radiolabelling with high radiochemical yield and purity. The radiolabeled compounds exhibited low protein binding and high stability in serum and tissue homogenates. In AFU, uptake was SIT1-dependent under iron-depleted conditions. MIC assays revealed moderate antifungal activity, superior to that of DFO or carboplatin alone. PET/CT imaging in a rat pulmonary aspergillosis model indicated rapid systemic distribution, exclusive renal excretion, and selective accumulation in infected lung tissue. A major in vivo metabolite, identified as free DFO-succinate, was detected shortly post-injection in serum and urine.3
In conclusion, Pt(IV)–DFO conjugates present a promising theranostic platform for targeted antimicrobial therapy and molecular imaging. Further optimization is needed to enhance antifungal potency and in vivo stability.
- 1. H. P. Varbanov, F. Kuttler, D. Banfi, G. Turcatti, P. J. Dyson, PLoS One, 2019, 14, e0211268.
- 2. S. Harringer, M. Hejl, E. A. Enyedy, M. A. Jakupec, M. S. Galanski, B. K. Keppler, P. J. Dyson, H. P. Varbanov, Dalton Trans., 2021, 50, 8167.
- 3. M. Kraihammer, H. P. Varbanov, K. Dvořáková Bendová, M. Petřík, A. Yap, H. Haas, C. Decristoforo, Eur. J. Med. Chem. (under review)