Poster Presentation 21st International Conference on Biological Inorganic Chemistry 2025
Peptidyl copper complexes mimicking laccase activity to trigger selective cytotoxic drug synthesis in cells (#488)
Over the past decades, biocompatible catalysts–prodrug pairs have been developed, with some reaching clinical trials.1 Among them, metal catalysts have been widely used to trigger the biorthogonal release of drugs.2 Peptidyl metal complexes, inspired by natural metalloenzymes, are interesting candidates in this context since they can selectively and efficiently catalyze reactions under physiological conditions (pH 7.4).3 Even though the examples of conjugated peptidyl metal complexes with a targeting moiety are scarce,4 they can be easily conjugated to enhance selectivity by increasing drug concentration in targeted cells while decreasing the uptake in healthy cells.
In this work, we aim at catalyzing the synthesis of a cytotoxic drug in cells from a non-toxic substrate by developing peptidyl copper complexes that mimic laccase, a copper enzyme catalyzing substrates oxidation through a 4-electron reaction while reducing dioxygen into water.5 Then, by conjugating the catalyst with a targeting peptide, we aim to improve the selectivity of the treatment.
Using a combinatorial approach associated with an activity-based screening3, we identified efficient complexes catalysing 2,6-dimethoxyphenol (DMP) oxidation, a laccase-type reaction that produces a colored intermediate. The selected complexes were then in depth characterized by a panel of analytical techniques allowing us to obtain key features (stoichiometry, association constants) as well as their catalytic activities. The selected complexes are now used to perform the in-cell oxidation of non-toxic 2,6-dimethoxyphenol to produce the cytotoxic 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethoxybiphenyl-4,4′-diol compound.6 The anti-tumoral activity is currently evaluated by standard viability bioassays (on cells and zebrafish model). The best peptidyl copper complex will be then conjugated with the adequate targeting peptide and the selectivity will be assessed.
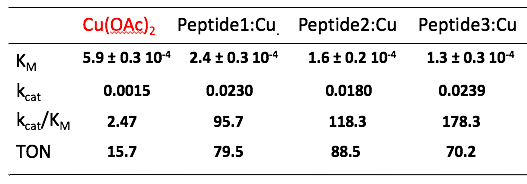
We successfully developed a highly efficient peptidyl-copper complex exhibiting laccase-type activity (see table). The selected complex is being studied to demonstrate its activity in cells, making it a promising candidate for the selective targeting of tumor cells.
- Kratz, F.; Abu Ajaj, K.; Warnecke, A. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs 2007, 16 (7), 1037–1058.
- Vong, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Chang, T.; Tanaka, K. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11 (40), 10928–10933.
- Coulibaly, K.; Thauvin, M.; Melenbacher, A.; Testard, C.; Trigoni, E.; Vincent, A.; Stillman, M. J.; Vriz, S.; Policar, C.; Delsuc, N. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60 (13), 9309–9319.
- Tomás-Gamasa, M.; Martínez-Calvo, M.; Couceiro, J. R.; Mascareñas, J. L. Nat Commun 2016, 7 (1), 12538.
- Brugnari, T.; Braga, D. M.; Dos Santos, C. S. A.; Torres, B. H. C.; Modkovski, T. A.; Haminiuk, C. W. I.; Maciel, G. M. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2021, 8 (1), 131.
- Concato, V. M.; Tomiotto-Pellissier, F.; Silva, T. F.; Gonçalves, M. D.; Bortoleti, B. T. D. S.; Detoni, M. B.; Siqueira, E. D. S.; Rodrigues, A. C. J.; Schirmann, J. G.; Barbosa-Dekker, A. D. M.; Costa, I. N.; Conchon-Costa, I.; Miranda-Sapla, M. M.; Mantovani, M. S.; Pavanelli, W. R. Chemico-Biological Interactions 2020, 326, 109133.