Poster Presentation 21st International Conference on Biological Inorganic Chemistry 2025
Correlation between the modification of the X ligands of the [Cu(IPr)X] series of complexes and their antileishmanial activity (#457)
Aims
Leishmaniasis is a NTD and its treatment presents several adverse effects. It’s well known that metal based compounds, like copper(I), can interact with parasitic biomolecules, which makes them an alternative to target specific molecules of the parasites. Cu(I) can be stabilized by IPr, an N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC), forming stable linear complexes1. In this study we investigate the influence of the halide trans to the NHC in the biological outcome of the series of complexes [Cu(IPr)X] (X = Cl, Br, and I).
Methods
In order to obtain the proposed complexes, a weak-base route mechanism was applied based on Santoro et. al studies2. After stirring for 24h at 60°C, the solution was filtered on celite, concentrated under vacuum, and pentane was added for precipitation, giving a white powder that was dried under vacuum (Figure 1).
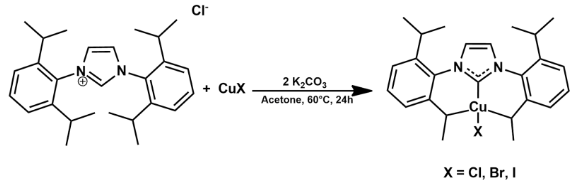
Figure 1: Santoro et. al synthesis procedure
Results
In the 13C NMR (Figure 2) spectrum we observe that there is a shift between the complexes, in which [Cu(IPr)I] has a larger shift (180.912 ppm), while [Cu(IPr)C] has a smaller shift (178.743 ppm). This behavior is consistent with Huynh´s observation3, as the addition of a donor ligand trans to NHC favors the shift of this carbon, leading to greater deshielding.
Preliminary DFT calculations of the charge distribution in these Cu(I) complexes support this interpretation.
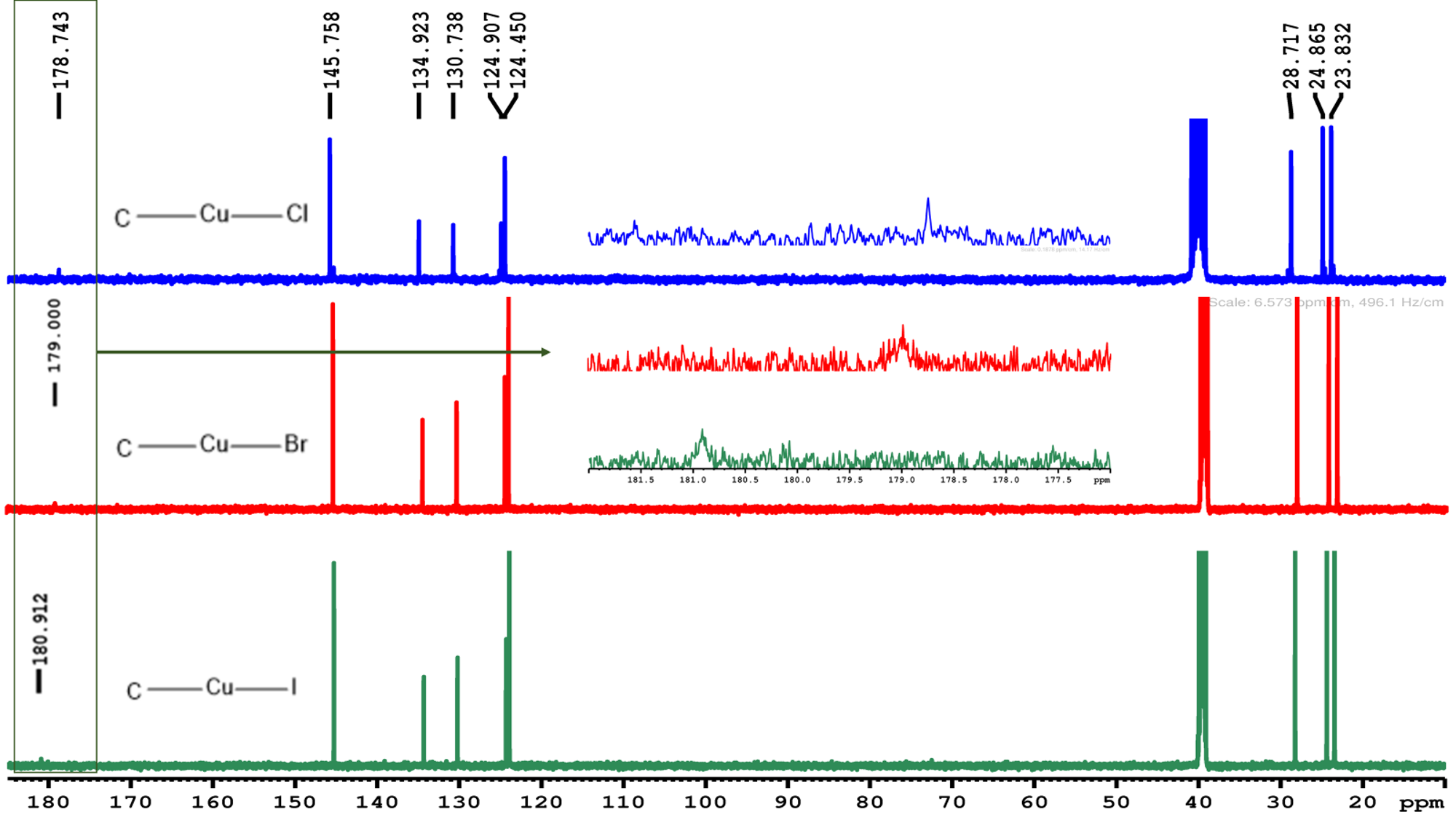
Figure 2: 13C NMR spectra of the complexes [Cu(IPr)X] in DMSO-d6, 300MHz.
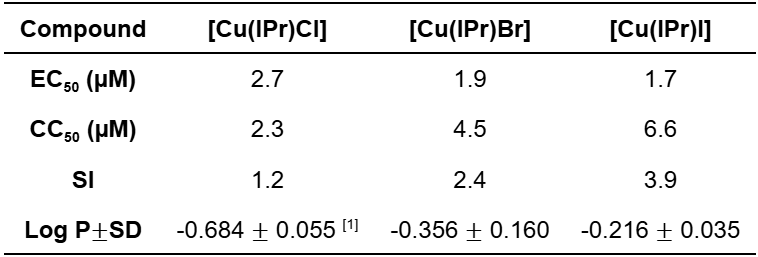
Table 1: Determination of the half maximal effective concentration (EC50) in L. amazonensis, half maximal cytotoxic concentration (CC50) in Bone Marrow Differentiate Macrophages, selectivity index (SI) and lipophilicity results (octanol/water partition coefficient).
Conclusion
The shifts in ¹³C NMR demonstrate iodine has the most deshielded carbon, suggesting less charge donation to the NHC. It is also possible to observe a correlation between the halides in lipophilicity and biological studies, which shows that the complex [Cu(IPr)I] is the most lipophilic compound and exhibits the highest selectivity index between the series studied.
- (1) FONTES, Josielle et al. Antileishmanial and Anti‐Chikungunya Activity of Cu(I)‐N‐Heterocyclic Carbenes. ChemistrySelect, 2022, 7.
- (2) SANTORO, Orlando et al. A general synthetic route to [Cu(X)(NHC)] (NHC = N-heterocyclic carbene, X = Cl, Br, I) complexes. Chem Commun, 2013, 49, 10483-10485.
- (3) Huynh, H. V. et al. 13C NMR Spectroscopic Determination of Ligand Donor Strengths Using N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes of Palladium(II). Organometallics, 2009, 28, 18, 5395–5404.